In the resources sector, safety often conjures images of PPE, pre-starts, and hazard reports, all critical, physical aspects of risk management. However, psychological safety is equally important and increasingly recognised under new codes of practice around psychosocial risks at work.
Mackay Safety’s latest innovation – a custom-developed payroll dashboard for a reputable drilling and rehabilitation company, Central Queensland Exploration (CQE) – is an example of what happens when organisations treat psychological health as seriously as physical safety. Built in partnership with CQE’s finance and safety teams, the project employed a work redesign approach to eliminate job stressors that had been quietly, yet consistently, affecting employee wellbeing.
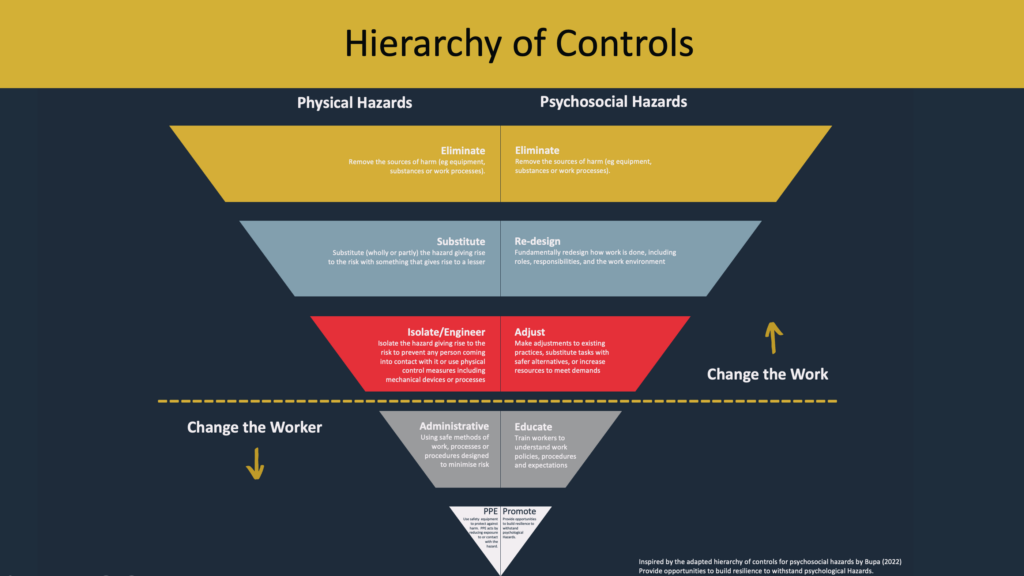
“Work pressure is the leading cause of psychosocial injuries in Australia,” Naomi explained. “And in high-cognition roles like payroll, especially when there’s little room for error, the mental load is significant.”
Rather than treating stress as an individual issue, CQE and Mackay Safety tackled the root cause: the design of the payroll process itself. Using the hierarchy of controls to guide decision-making, Mackay Safety collaborated with CQE to develop a custom payroll dashboard that effectively mitigated key psychosocial risks by automating manual tasks, reducing emotional strain, and enhancing role clarity.
“We weren’t just digitising for efficiency – we were reducing harm,” said Mick Storch, founder and managing director of Mackay Safety. “It was about building systems that support people to do their jobs without unnecessary stress.”
The dashboard integrates with CQE’s existing 4PS software and accounting platform. Timesheet data is now entered once via a mobile-friendly form, approved digitally, and automatically transferred into payroll, eliminating emails, rekeying, and errors. For field staff, it means clearer expectations and smoother pay cycles. For finance, it means better workflows and fewer headaches.
Since implementing the system, CQE has halved payroll processing time – from three days to around one and a half – while improving accuracy and team satisfaction.
Importantly, the solution wasn’t a one-size-fits-all product. It was a collaborative development tailored to CQE’s unique needs.
“You don’t just get software with Mackay Safety – you get a partner who listens, adapts, and genuinely cares about outcomes,” said Simon Harris, CQE HSE Manager.
“The time savings were immediate, but what’s been more powerful is the change in atmosphere,” said Sidney Potter, CQE Accounts Administrator. “People aren’t stressed about delays or chasing approvals. They’re more confident in the process – and in us.”
These efficiencies have also freed up time for more value-adding work. As CQE HSE Manager Simon Harris observed, the gains from streamlined systems multiply in ways that are hard to quantify – building quiet confidence across teams and creating a flow-on effect at the coalface.
This success mirrors other changes Mackay Safety has delivered for CQE using its 4PS software. From digital asset management to compliance workflows and pre-starts, the company’s approach consistently reduces both physical and psychological hazards by improving work design.
While the dashboard itself focused on payroll, the ripple effects have improved safety culture across CQE. Team members feel heard, processes feel fairer, and communication flows more easily between departments.
As Naomi Armitage noted in her keynote speech at the Resource Industry Network Safety Conference about designing effective psychosocial risk management controls, focusing on work design, many workplace tensions, from interpersonal conflict to disengagement, stem from unclear roles, procedural injustice, or avoidable stressors. Mackay Safety’s digital systems reduce these “work factors” by increasing transparency and reducing friction.
“Too often, businesses wait for issues like burnout or disengagement to surface before acting,” Naomi Armitage said. “But the best controls eliminate exposure, which is exactly what this payroll dashboard has done.”
Simon Harris also noted that a single system improvement, when thoughtfully implemented, can drive widespread cultural change, enabling businesses like CQE to handle future growth without sacrificing wellbeing.
This dual emphasis on mental and physical safety reflects Mackay Safety’s broader philosophy. Across all client projects, the goal is the same: to make safety second nature.
The CQE payroll dashboard is already having an impact on other areas of the business. Similar design principles are now being explored to manage training, equipment tickets, and role-based access, all through a psychosocial lens.
Mackay Safety’s ability to evolve its tools in partnership with clients is what makes its safety impact so enduring. Mick Storch believes this consultative, user-led approach will become even more vital as the industry faces growing pressure to address psychological risk.
“Safety isn’t just hard hats and high-vis anymore,” he said. “It’s clarity, confidence, and culture. And those things start with how you design your work.”
Mackay Safety’s payroll dashboard project with CQE demonstrates how innovation, collaboration, and a people-first mindset can drive real change in workplace safety. By eliminating psychosocial hazards at the systems level, Mackay Safety has enhanced efficiency and contributed to creating a safer and healthier work environment.
--
Thank you to the team at CQE for sharing their experience partnering with Mackay Safety and 4PS software.
Contact Mackay Safety today on 07 4944 1272 or explore the website to learn more about how we can support your operations with services and technology that ensure you keep on top of your safety and compliance requirements.
Founded in 1994 as Capricorn Drilling Services, Central Queensland Exploration (CQE) has grown into one of Queensland’s most respected names in drilling and rehabilitation. Following strategic acquisitions in 2022 and 2024, the company consolidated under a single banner and now operates a fleet of 20 drill rigs, with a workforce exceeding 130 people.
CQE services major mining clients across the Bowen Basin and runs crews on ‘two week on, two week off rosters, creating a constant need for efficient onboarding and induction processes. As Human Resources (HR) Manager, Taylah Neal oversees CQE’s end-to-end HR function and works closely with Mackay Safety and the 4PS team on digital solutions that streamline operational workflows.
Most recently, Taylah led the rollout of the new 4PS Software employee induction system, which aimed to modernise the company’s onboarding experience, strengthen compliance, and significantly reduce manual handling.
Taylah said: “I’ve been working in collaboration with 4PS for quite some time, but most recently I’ve been working on the 4PS induction system and having that process streamline our induction process. It is incredible.”
Before adopting 4PS, CQE’s induction system was technically online but extremely manual behind the scenes. The process created a heavy administrative load, confusion for new employees, and ongoing frustration for HR. This was not an ideal introduction to the business for new employees.
Challenges for administration
Under the old system, new starters received between 15 and 20 separate emails, each containing an individual induction module. HR then had to check every induction manually, cancelling and resending incomplete modules and regularly chasing personnel for updates. Once an induction was finally completed, the team had to manually convert it into a certificate and save it into both SharePoint and 4PS, one at a time. This created significant bottlenecks for administration, with staff often arriving on Monday mornings to inboxes flooded with 60 or more emails from inductions completed over the weekend. As Taylah noted, “It was quite labour-intensive and time-consuming. Creating those certificates and saving 15 individual files into 4PS is not a quick task.”
Challenges for new starters
For new employees, the experience was equally difficult. The sheer volume of separate emails made it hard to keep track of which inductions had been completed and which were still outstanding. The system delivered modules one at a time with no dashboard or central view, leaving new starters with no clear sense of their progress. This fragmented approach created unnecessary stress and a poor first impression, particularly for drillers and offsiders who are highly capable on the tools but not always tech savvy. As Taylah explained, “When they received 15 to 20 emails, they would think they’ve completed them, but they’d lost track of which ones they had done and hadn’t. It just didn’t give a very professional vibe to the start of employment with CQE.”
Challenges updating induction content
Even small changes were time-consuming. Updating a single induction required converting PowerPoint slides to JPEGs and uploading them one at a time into the old system.
“I lost hours and hours just updating one induction. It was extremely time consuming.”
Limited software support
Support for the previous system was limited to an offshore chat tool with no direct contact.
“There was no phone number, no one to talk to. Having a personal relationship with someone just up the road is very valuable.”
CQE needed a modern, centralised induction system that would simplify onboarding, remove manual effort and scale with the company’s ongoing growth.
CQE partnered with Mackay Safety and the 4PS Software team to implement a dedicated 4PS induction system designed to automate, streamline, and modernise onboarding processes.
Single email onboarding with role-based induction groups
Instead of issuing inductions individually, Taylah now assigns each new starter to a role-based induction group.
“You just select the group, and it sends one email with a magic link. They log in and can see all the inductions they need to complete on one page.”
Automated certificates and filing
Taylah worked with 4PS to design a standardised certificate template. Once an induction is completed, the system automatically generates the certificate, files it into the employee’s 4PS record and removes all manual processing.
“It now automatically saves the certificate with the relevant information into their employee file on 4PS. It is a game changer.”
Simple, fast content updates
With inductions now linked through Google Drive, Taylah can update content herself.
“I updated three inductions yesterday. I just updated the PowerPoint, converted it to a PDF, put it in Google Drive and refreshed the link. What a huge difference.”
Responsive, local support
Taylah highlighted the partnership with Mackay Safety and 4PS as a standout advantage.
“They’re amazing. Barb has been incredibly helpful and always prompt to reply. Even if she’s out of the office, she sends a message. Having that personal relationship is very valuable.”
Together, these improvements have delivered clear and measurable benefits for CQE, with outcomes that span efficiency, user experience, and long-term capability. These include:
--
Thank you to Taylah Neal for sharing her experience partnering with Mackay Safety and 4PS software.
Contact Mackay Safety today on 07 4944 1272 or explore the website to learn more about how we can support your operations with services and technology that ensure you keep on top of your safety and compliance requirements.

Serra Drilling is a family-owned and operated company based in the Atherton Tablelands, North Queensland. Established in 1970, the business has provided specialist drilling services across Queensland and interstate for over five decades. Serra Drilling employs both highly experienced water wells and exploration drillers. With deep expertise and state-of-the-art equipment, the company consistently delivers some of the most technically challenging drilling programs safely and efficiently. The company takes pride in the quality of its work and offers clients safe and competitive drilling services.
Their service offering includes large diameter water production bores, dewatering bores, stock and domestic water bores, groundwater monitoring bores, piezometer installations, exploration drilling, and pump testing.
As a third-generation business operating across multiple sectors, including mining, agriculture, construction, and government, Serra Drilling required a streamlined, reliable, and cost-effective system to manage safety and compliance documentation across geographically dispersed and fast-moving projects.
Their previous systems were fragmented, with manual paper forms often getting lost in trucks or failing to return to the office. Digital tools they had previously considered or trialled were either too complex, too expensive, or poorly suited for small to mid-sized operators.
In March 2023, Serra Drilling turned to Mackay Safety and implemented the 4PS Software suite after a successful demonstration, comprising their:

• Safety management plan
• Membership and advisory support
• 4PS Software core system including 4P Forms
• 4PS mobile app
• Dropbox integration.
This integrated solution allowed the team to digitise safety forms, sync field data with the office, track asset maintenance, manage certificates, and easily share records with clients — all while keeping the system cost-effective and user-friendly for their team. The 4PS software installed from Mackay Safety was customised to Serra Drilling’s specific needs and is continually updated to ensure relevancy and apply the latest technological advancements.
Since partnering with Mackay Safety and implementing the 4PS Software system, Serra Drilling has transformed its approach to safety, compliance, and operations, achieving significant gains in efficiency, productivity, and peace of mind.
 A standout achievement has been gaining ISO certification – a feat the company had never attempted before due to the complexity and manual nature of its previous systems. ISO certification formally recognises that a business meets internationally agreed standards for consistency, reliability, and quality, developed by the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO). It’s a strong trust signal for clients in sectors such as mining, construction, and government – and is often essential for winning contracts.
A standout achievement has been gaining ISO certification – a feat the company had never attempted before due to the complexity and manual nature of its previous systems. ISO certification formally recognises that a business meets internationally agreed standards for consistency, reliability, and quality, developed by the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO). It’s a strong trust signal for clients in sectors such as mining, construction, and government – and is often essential for winning contracts.
With the support of Mackay Safety, Serra Drilling successfully passed an independent audit and gained recognition for its compliance.
“We probably wouldn’t have applied for ISO accreditation if it weren’t for 4PS and Mackay Safety,” said Serra Drilling General Manager, Mark Serra. “With our previous systems, it would have taken five years to achieve the level of documentation needed – if it happened at all.”
The operational impact has been equally impressive. By digitising safety processes and automating reporting, Serra Drilling has avoided the need to hire extra administration or safety staff.
“We’d need another full-time safety person in the office to do what we’re doing now at minimum, and that’s easily one salary saved at around $150,000,” Mark said.
Productivity has soared. The team now handles four times the volume of safety, compliance, and reporting work, all achieved without expanding the workforce.
“We’re doing four times the amount of work with the same people.”
 Real-time reporting has improved response times across projects, with incidents reported instantly via the app.
Real-time reporting has improved response times across projects, with incidents reported instantly via the app.
“I’ll get an incident report via email from the app before I even get a phone call.”
Asset maintenance has become more efficient, with automated links between field reports, asset registers, and certificate renewals.
“The system helps us manage both maintenance and safety – two critical aspects of our business.”
According to Mark, what truly sets 4PS Software apart is the hands-on service and customisation Mick and his team at Mackay Safety provide.
“We pay for what we need with Mackay Safety — and sometimes what has been developed to assist us helps other companies and vice versa. It works incredibly well,” Mark said.
This collaborative and tailored approach has been key to Serra Drilling’s long-term success with the platform.
“4PS Software and Mackay Safety’s support services have changed the way we do business. The system is user-friendly, has saved us time and money, and has helped us achieve ISO certification. Our productivity has quadrupled – and we didn’t need to hire anyone new to achieve this.”
--
 Thank you to Mark Serra for sharing his experience with Mackay Safety and 4PS software.
Thank you to Mark Serra for sharing his experience with Mackay Safety and 4PS software.
Contact Mackay Safety today on 07 4944 1272 or explore the website to learn more about how we can support your operations with services and technology that ensure you keep on top of your safety and compliance requirements.
As many businesses discover, not only is workplace health and safety (WHS) compliance a legal obligation; it’s a critical aspect of fostering a safe and productive work environment.
Proactive WHS management helps businesses reduce the risk of accidents, enhance employee well-being, and improve overall operational efficiency.
By prioritising WHS, organisations can build trust among their workforce, reduce downtime from incidents, and avoid costly penalties or reputational damage.
A commitment to proactive WHS compliance is an investment in the longevity and success of any business.
In this article, Mackay Safety explores the best practices for WHS compliance and provides advice about how to engage in workplace hazard prevention.
Modern workplaces face a variety of hazards, ranging from physical risks like slips, trips, and falls to ergonomic challenges caused by prolonged desk work.
Other common risks include exposure to hazardous substances, electrical hazards, and mental health stressors.
Identifying these hazards early is crucial to creating an environment where employees feel secure and protected.
Regular workplace assessments and open communication between management and staff play an essential role in mitigating these risks.
Additionally, implementing comprehensive training programs ensures employees are equipped to handle potential dangers, fostering a culture of safety and well-being.
By addressing both physical and psychological risks, organisations can promote productivity and morale while reducing the likelihood of incidents.
Risk management tools are indispensable in identifying and addressing workplace hazards, forming a crucial part of comprehensive risk management strategies.
Tools such as safety audits, hazard identification checklists, and digital incident reporting systems enable businesses to track and manage risks effectively.
These tools also help in prioritising corrective actions and allocating resources where they’re most needed, ultimately reducing the likelihood of incidents.
To minimise risks, organisations should develop and enforce robust safety policies tailored to their specific industries.
Regular safety inspections, clear and visible signage, and the provision of accessible personal protective equipment (PPE) are fundamental practices that support a safe work environment.
Additionally, fostering open communication channels is crucial as it empowers employees to report potential hazards or unsafe conditions without hesitation, creating a culture of share responsibility and continuous improvement.
By prioritising WHS and implementing effective workplace safety practices, organisations can build trust among their workforce, reduce downtime from incidents, and avoid costly penalties or reputational damage.
WHS risk assessment tools, such as digital compliance software, simplify the process of identifying and managing workplace hazards.
These tools allow businesses to assess risks in real time, track corrective actions, and maintain compliance records.
Integrating digital tools into daily operations ensures a proactive approach to workplace safety.
One such powerful tool is Mackay Safety’s 4PS software, which stands for Predict, Prevent, Protect, and Perform.
This software is designed to enhance workplace safety by providing a comprehensive suite of features including real-time risk assessments, automated compliance tracking, and detailed incident reporting.
The predictive analytics component of the 4PS software assists in forecasting potential hazards before they manifest, while the preventive measures help in mitigating risks proactively.
A culture of safety always starts at the top.
Leadership must demonstrate a commitment to WHS compliance by setting clear expectations and leading by example.
Encouraging employee involvement in safety initiatives, such as forming WHS committees, helps instil a shared sense of responsibility for workplace safety.
When leaders actively prioritise safety, it reinforces the importance of adhering to policies and creates a workplace where employees feel valued and protected.
Transparent communication about safety goals and progress fosters trust and ensures everyone understands their role in maintaining a safe environment.
Additionally, recognising and rewarding proactive safety efforts can motivate employees to remain vigilant and engaged in fostering a positive safety culture.
Examples include:
These types of rewards not only reinforce the importance of safety but also foster a positive, engaged work environment where employees feel motivated to contribute.
Comprehensive training programs equip employees with the knowledge and skills to identify and mitigate risks.
Regular refresher courses and hands-on training sessions ensure that safety practices are consistently upheld.
Training also empowers employees to act confidently in emergencies, reducing the potential for injury or damage.
By fostering a culture of continuous learning, businesses can adapt to new safety challenges and maintain a resilient workforce.
The rise of digital tools has revolutionised Workplace Health and Safety compliance.
Platforms for incident reporting, safety training modules, and automated risk assessments streamline processes and improve accuracy.
Real-time data analytics provide insights into trends, enabling businesses to address emerging risks proactively.
By harnessing technological advancements, organisations can not only ensure compliance but also foster a culture of safety that permeates every level of the workforce.
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as incident rates, near-miss reports, and employee training completion rates helps organisations measure the effectiveness of their WHS initiatives.
In addition to these metrics, it’s beneficial to incorporate both leading and lagging indicators.
Leading indicators, such as the number of safety audits conducted or the frequency of safety meetings, are proactive measures that can predict and prevent incidents.
Lagging indicators, like lost-time frequency rates, reflect past incident and help access the outcomes of safety initiatives.
Regularly reviewing these metrics ensures continuous improvement and demonstrates a commitment to maintaining a safe workplace.
For more detailed guidance on setting and measuring WHS KPIs, Safe Work Australia’s report, Measuring and Reporting on Work Health and Safety, provides a comprehensive framework.
Proactive WHS compliance is essential for minimising workplace risks and fostering a culture of safety.
By recognising common hazards, implementing effective safety practices, leveraging digital tools, and prioritising training and culture, organisations can create a safer and more productive work environment.
Businesses are encouraged to adopt these best practices and invest in the tools and training needed to ensure long-term WHS success.
For tailored guidance and expert support in proactive WHS management, contact Mackay Safety on 07 4944 1272 to help you builder a safer and more resilient workplace.
Mackay Safety helps clients throughout Australia win tenders, provide safety advice, and as safety and risk management experts, they can help steer your business in the right direction even if you’re not sure exactly how to get started.
Workplace safety has always been a top priority for organisations, but challenges of the modern era demand a more innovative and proactive approach.
Increasing complexities, evolving hazards, and regulatory demands make effective safety management essential.
Incident Cause Analysis Method (ICAM) investigations are a proven tool for identifying root causes and preventing incidents.
In the digital age, advanced platforms are transforming ICAM processes, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness.
This blog explores the significance of ICAM, the role of digital tools, and how organisations can use these innovations to improve workplace safety.
The Incident Cause Analysis Method (ICAM) is a systematic approach to investigating workplace incidents, designed to uncover not only what occurred but also the underlying reasons behind it.
By examining systemic issues and human factors, ICAM addresses root causes rather than just surface-level problems, leading to significant and lasting safety improvements.
This method is critical for organisations aiming to enhance workplace safety, mitigate risks, and adhere to safety regulations.
ICAM is especially beneficial in high-risk industries like construction, manufacturing, and healthcare, where the consequences of safety failures can be severe.
At its core, ICAM is built on two guiding principles:
Historically, ICAM investigations were conducted using manual methods, such as physical documentation, spreadsheets, and in-person interviews.
While effective, these processes were often time-consuming, prone to human error, and limited in scalability.
Digital platforms in workplace safety include tools such as incident management software, data analytics platforms, and cloud-based collaboration systems.
These technologies help organisations monitor hazards, manage incidents, and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Workplace safety management has evolved significantly over the past two decades.
Traditional, paper-based methods have given way to digital solutions that offer real-time insights, automation, and advanced analytics.
This transformation has enabled businesses to respond more effectively to safety challenges while reducing administrative burdens.
Digital transformation brings numerous benefits, including:
Digital platforms are transforming ICAM processes by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration.
Here are key ways they optimise each stage of the process:
Innovative digital tools are revolutionising ICAM by streamlining processes and enhancing collaboration.
Here are some examples of cutting-edge solutions driving these improvements:
Digital platforms minimise human error and ensure consistent application of ICAM methodologies.
Automated data collection and analysis tools eliminate inconsistencies, leading to more reliable investigation outcomes.
Digital tools streamline every step of the ICAM process, from evidence gathering to reporting.
This efficiency saves time, reduces administrative burdens, and allows organisations to allocate resources more effectively.
By integrating safety protocols and legal requirements into digital platforms, organisations can ensure adherence to WHS regulations.
Automated audit trails and compliance checks simplify regulatory reporting and reduce the risk of penalties.
Digital platforms promote a culture of continuous improvement by providing insights into recurring issues, tracking the effectiveness of corrective actions, and encouraging employee participation in safety initiatives.
Despite their benefits, digital platforms often face challenges during implementation:
Adopting digital solutions for ICAM comes with challenges, but effective strategies can ensure a smooth transition while maximising the benefits such as:
At the same time, emerging technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT are transforming safety management, paving the way for smarter, more initiative-taking approaches to workplace safety.
Strong leadership is essential for driving digital transformation.
Leaders must champion the adoption of digital ICAM platforms, communicate their value to employees, and address concerns proactively.
Advanced technologies are transforming how workplace safety is managed, enabling smarter and more proactive solutions. Key innovations shaping the future of safety include:
By leveraging these technologies, businesses can create safer and more responsive work environments.
As digital tools become more sophisticated, their integration into WHS systems will continue to grow.
We can expect advancements in data visualisation, real-time monitoring, and predictive safety models.
To stay ahead, organisations must:
In conclusion, digital platforms are revolutionising how organisations conduct ICAM investigations, transforming them into more efficient, accurate, and actionable processes.
By leveraging these tools, businesses can uncover root causes, address systemic issues, and build a proactive safety culture.
ICAM remains critical to achieving workplace safety by focusing on prevention and system improvement.
However, embracing digital transformation is essential for organisations aiming to stay competitive and compliant in an evolving safety landscape.
By adopting digital platforms, companies can ensure safer workplaces, protect employees, and meet the challenges of modern safety management. Take the first step toward a safer future today.
At Mackay Safety our workplace health and safety management consultants and advisors specialise in providing expert guidance and innovative solutions for implementing ICAM investigations and digital safety platforms.
Our 4PS is specifically designed to enhance safety and risk management by offering:
Structured investigative support
4PS software provides a systematic framework that aligns well with the ICAM methodology, ensuring thorough investigation into incidents by identifying root causes and contributing factors.
Integrated tools for analysis
It integrates advanced tools like flowcharts, cause-and-effect diagrams, and data categorisation, which are crucial for visually mapping out the sequence of events and identifying systemic issues.
Expert knowledge base
The platform often includes built-in guidance based on industry best practices and lessons learned from past incidents, which helps investigators make informed decisions.
Collaborative features
ICAM investigations usually involve input from multiple stakeholders. 4PS software facilitates collaboration, ensuring all relevant parties can contribute efficiently.
Actionable recommendations
Once root causes are identified, 4PS helps in developing practical and innovative corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
Compliance and reporting
The software simplifies compliance with safety regulations and provides customisable reporting features for presenting findings to stakeholders.
Contact Mackay Safety on 07 4944 1272 or visit their website at mackaysafety.com.au to learn how they can support your organisation in achieving its safety goals.